iTSSe
TSS
A D V A N C E D M A T E R I A L S & P R O C E S S E S | M A Y / J U N E 2 0 1 7
4 2
iTSSe
TSS
FEATURE ARTICLE
8
F
ocused ion beam (FIB) systems are selectively used in
cold spray coating characterization to gather information
on the nature of splat formation, single splats, multiple
splats, or the coating-substrate interface. FIB resembles scan-
ning electron microscopy (SEM) except that instead of using a
focused beamof electrons to raster the sample surface, it uses
a focused beam of ions (usually gallium) either to image the
sample (using low-beam currents) or to remove material by
sputtering it away (high currents).
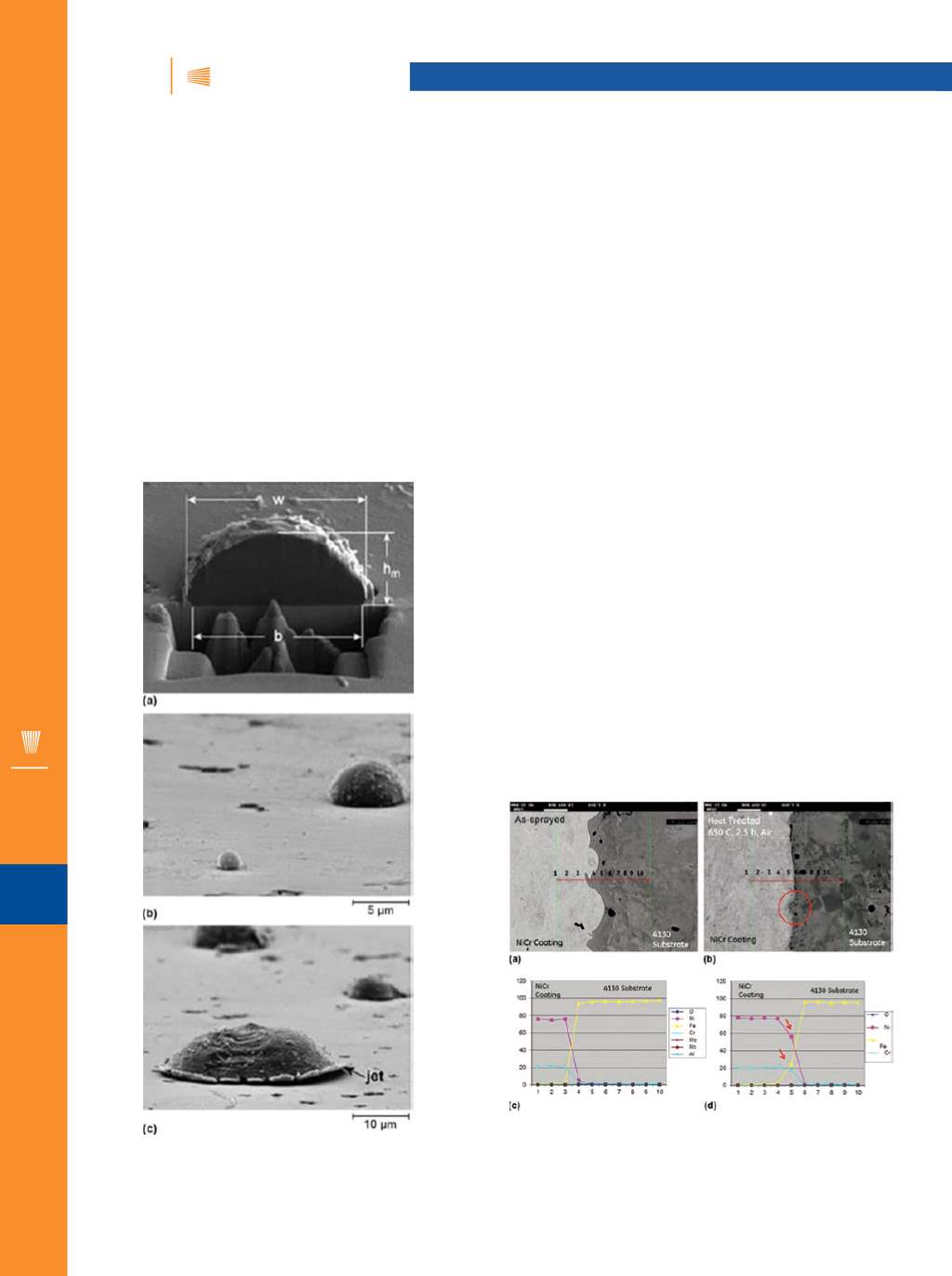
King and Jahedi
[1]
studied the effect of particle size and
bonding for aluminum and copper particles and were able to
make use of FIB machining to prepare sample sections and
then view and analyze them by means of SEM (Fig. 1a). The
particle-flattening ratios could be determined accurately us-
ing the FIB sections and used as inputs to feed into a model.
Smaller particles were seen with a higher bow shock effect in
the gas flow and exhibited greater resistance to deformation
on impact. This result was further validated using an SE image
with a stage tilt in the SEM
!
75° to precisely estimate the base
and apex of individual particles (Fig. 1b).
COLD SPRAY: ADVANCED CHARACTERIZATION
METHODS—FOCUSED ION BEAM MACHINING
AND ELECTRON PROBE MICROANALYSIS
This article series explores the indispensable role of characterization in the
development of cold spray coatings and illustrates some of the common
processes used during coatings development.
Dheepa Srinivasan, GE Power, GE India Technology Center, Bangalore
Fig. 1
— (a) Focused ion beam/scanning electron microscopy
image of aluminumparticle dissected using Ga ions.
(b, c) Secondary electron micrographs of aluminumparticles adher-
ing to ceramic (lead-zirconium titanate) surface
[1]
.
Fig. 2
—Representative scanning electron micrographs showing
Ni-20Cr coating on AISI 4130 steel substrate interface, (a) as sprayed
and (b) aer heat treatment. (c, d) Corresponding electron probe
microanalysis elemental profiles indicating the interdi¥usion of
elements at the interface
[2]
.