iTSSe
TSS
A D V A N C E D M A T E R I A L S & P R O C E S S E S | M A Y / J U N E 2 0 1 7
3 8
iTSSe
TSS
FEATURE ARTICLE
4
E
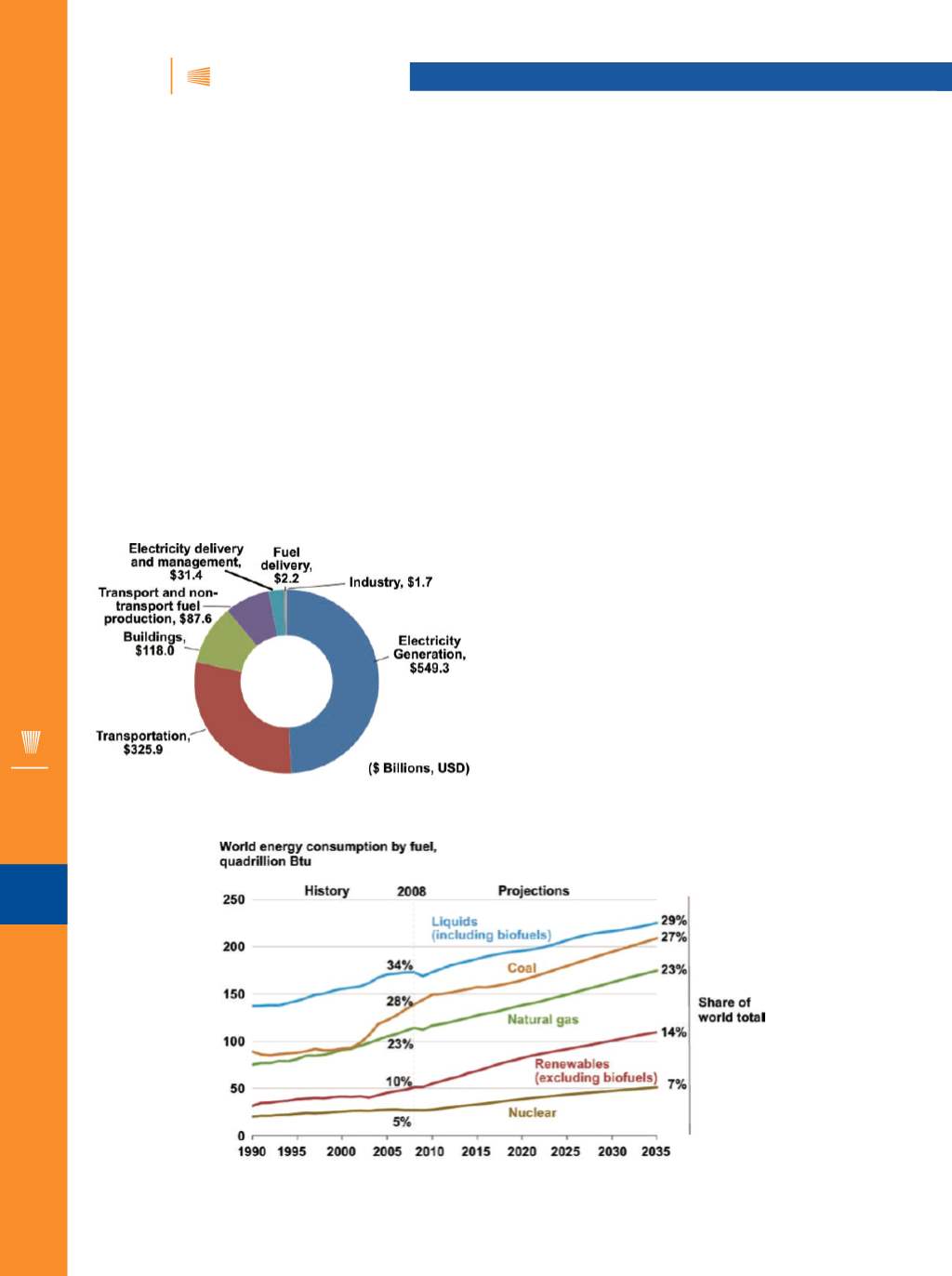
nergy gluttony represents a $1.1 trillion global market.
Electricity generation accounts for roughly half of this
energy revenue (Fig. 1), with 85% of worldwide con-
sumption dominated by traditional energy generation from
liquids, coal, and natural gas. Figure 2 shows it is anticipated
that these energy sources will be reduced to 79% as they are
displaced by renewable resources. The global advanced ener-
gy market is highly complex and consists of a wide variety of
technologies continually displacing each other as they reach
different levels of maturity.
WE NEVER HAVE ENOUGH ENERGY
Thermal spray plays a latent role in many energy generation applications. Strong
R&D commitment is required to further expand its technological envelope.
Christopher C. Berndt, FASM,* and Andrew Ang*
Swinburne University of Technology, Australia
Each country’s productivity (GDP), financial stability, and
overall economy are tied to the amount of electrical energy
generated. These numbers range from about $45K per capita
(for U.S., Japan, France, Germany, UK, and Australia) to $5K
per capita (for China, India, and Brazil)
[3]
. The corresponding
primary energies per capita are 350 and 50 in gigajoule
(
GJ),
respectively, for these country groups. A distinct positive cor-
relation exists between GDP and energy use per capita.
Thus, energy production is vital to driving a nation’s
economy. Power generation authorities want to design plants
to ensure continuous supply during periods of peak demand.
Power shortages lead to inefficiencies,which insomecountries
leads to political debates and restructuring of government
portfolios. Infrastructure costs of building and maintaining
a power plant and its associated network run into billions of
dollars. Materials engineering and materials selection are
critical in cutting lifecycle costs and retaining sustainability.
THE LATENT ROLE OF THERMAL SPRAY
Thermal spray (TS) plays many important roles with re-
gard to power generation. For example, it contributes to the
efficiency gains and infrastructure maintenance of energy
generation equipment. This is covered in the literature within
many technical and scientific reports
[4]
and reviews
[5,6]
, with
*Member of ASM International
Fig. 1
— Advanced energy revenue by segment in worldmarkets
[1]
.
Fig. 2
—Renewables are the fastest growing source of energy consumption
[2]
.