A D V A N C E D M A T E R I A L S & P R O C E S S E S | M A R C H 2 0 1 5
2 0
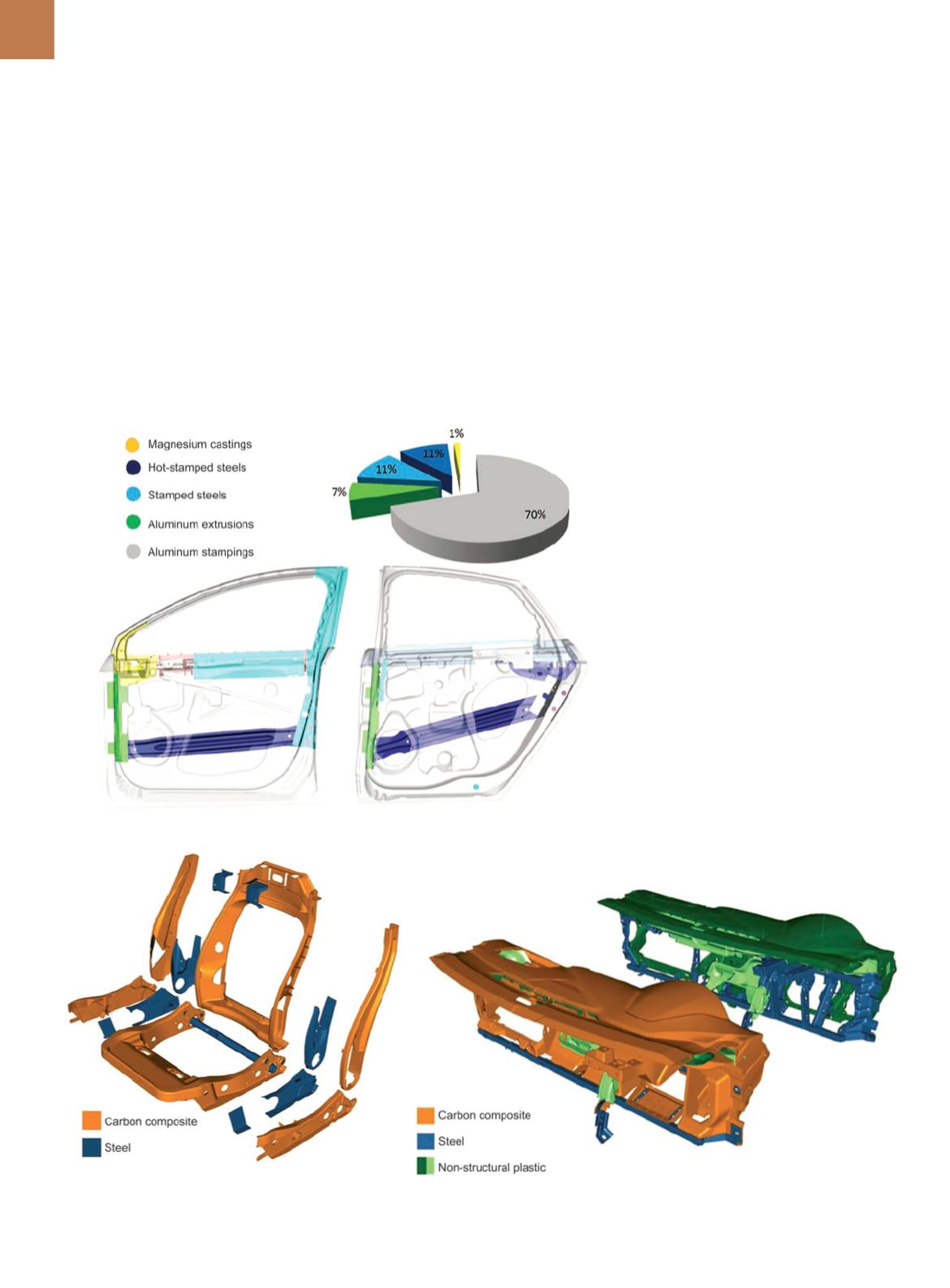
a cast magnesium sail (mirror mount)
part on the front doors. The Fusion
hood is already made of aluminum, so
only a small amount of weight is saved
using the aluminum hinges and latch
housing. The closure-in-white design
(69 kg) reduces 29 kg (30%) from the
2013 Fusion weight. The front door-in-
white, which includes a magnesium
sail casting, an extruded and machined
aluminum hinge pillar reinforcement,
stamped aluminum, stamped steel,
and a boron intrusion beam weighs
10.7 kg, which equals a 35% reduction
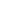
(5.9 kg). Figure 2 illustrates the material
distribution for the side doors.
Door designs also include cast
aluminum hinges, tape-on secondary
dynamic seals, and lightweight glaz-
ing. Laminated hybrid glazing reduc-
es the movable glazing from 13.8 kg
(4.3 kg front and 2.6 kg rear) by 4.7 kg
(34%). The door glazing is made up of a
1.8-mm layer of tempered (soda lime)
glass and a 0.8 mm acoustic PVB (poly-
vinyl butyral) layer strengthened with
a 0.7 mm chemically toughened glass
layer (Corning Gorilla Glass). Side door
glazings use a chemically toughened
glass layer located on the exterior
side with tempered glass on the inside
surface.
The fixed glazing includes a lami-
nated hybrid windscreen with a weight
of 9.1 kg—a 36% (5.1 kg) weight savings
from the prior Fusion windscreen with
an additional 4.5-mm-thick polycar-
bonate backlite that weighs just 5.9 kg—a
27% savings. The layered laminate on
the windshield is the same composition
as the side door glazing, but the chemi-
cally toughened glass layer is on the in-
terior. An additional 2.2 kg (15%) reduc-
tion from the functional and black trim,
enabled by using chemically foamed
plastics and 0.4 kg (~20%) in each of
four window regulators, increases the
overall weight savings.
BODY INTERIOR AND
CLIMATE CONTROL
The greatest savings in the body
interior and climate control systems
come from the seats and instrument
panel. Of the 45 kg saved in this system,
36 kg comes from carbon fiber compos-
ite use in structural portions of the seats
and instrument panel. The additional
9 kg of weight savings are made possi-
ble through use of chemically foamed
plastics for interior trim that eliminate
the dual control mode in the HVAC sys-
tem. These chemically foamed plastics
are created using catalysts introduced
during the injection mold process, under
controlled conditions that result in a thin
solid outer skinwith a foamed inner core.
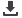
Seat structures made of carbon fi-
ber composite along with reduced foam
and lightweight back panels reduce the
Fig. 2 —
MMLV design door-in-white materials.
Fig. 3 —
Carbon fiber composite seat parts and
material distribution.
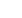
Fig. 4 —
Fusion and MMLV design instrument panel beams and HVAC ducts.