iTSSe
TSS
A D V A N C E D M A T E R I A L S & P R O C E S S E S | A P R I L 2 0 1 6
4 8
iTSSe
TSS
10
FEATURE ARTICLE
COLD SPRAY: ADVANCED
CHARACTERIZATION METHODS—PART I
This new article series explores the indispensable role of characterization in the development of cold
spray coatings and illustrates some of the common processes used during coatings development.
Dheepa Srinivasan,
GE Power, GE India Technology Center, Bangalore
M
aterials characterization is an inherent aspect of the
cold spray coating evaluation process. Characteriza-
tion of as-sprayed microstructures enables develop-
ment of an understanding of the thermomechanical evolution
of the coating and elucidates the bonding mechanisms both
within the coating and at the coating-substrate interface. Eval-
uating coating residual stress and coating relaxation behavior
after thermal treatments is imperative to establish the reli-
able functionality of the coating for the proposed application.
Microstructural characterization methods including optical
microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, transmission elec-
tronmicroscopy, electronbackscatter diffraction, andelectron
probe microanalysis are integral to understanding the highly
nonequilibriumprocess that enables formation of thick adher-
ent coatings via severe plastic deformation of metal powders.
Microhardness, nanoindentation, and residual stress analysis
add to a more complete understanding of the formed coating.
This article series will explore the indispensable role of
characterization in the development of cold spray coatings
and will illustrate some of the common processes used during
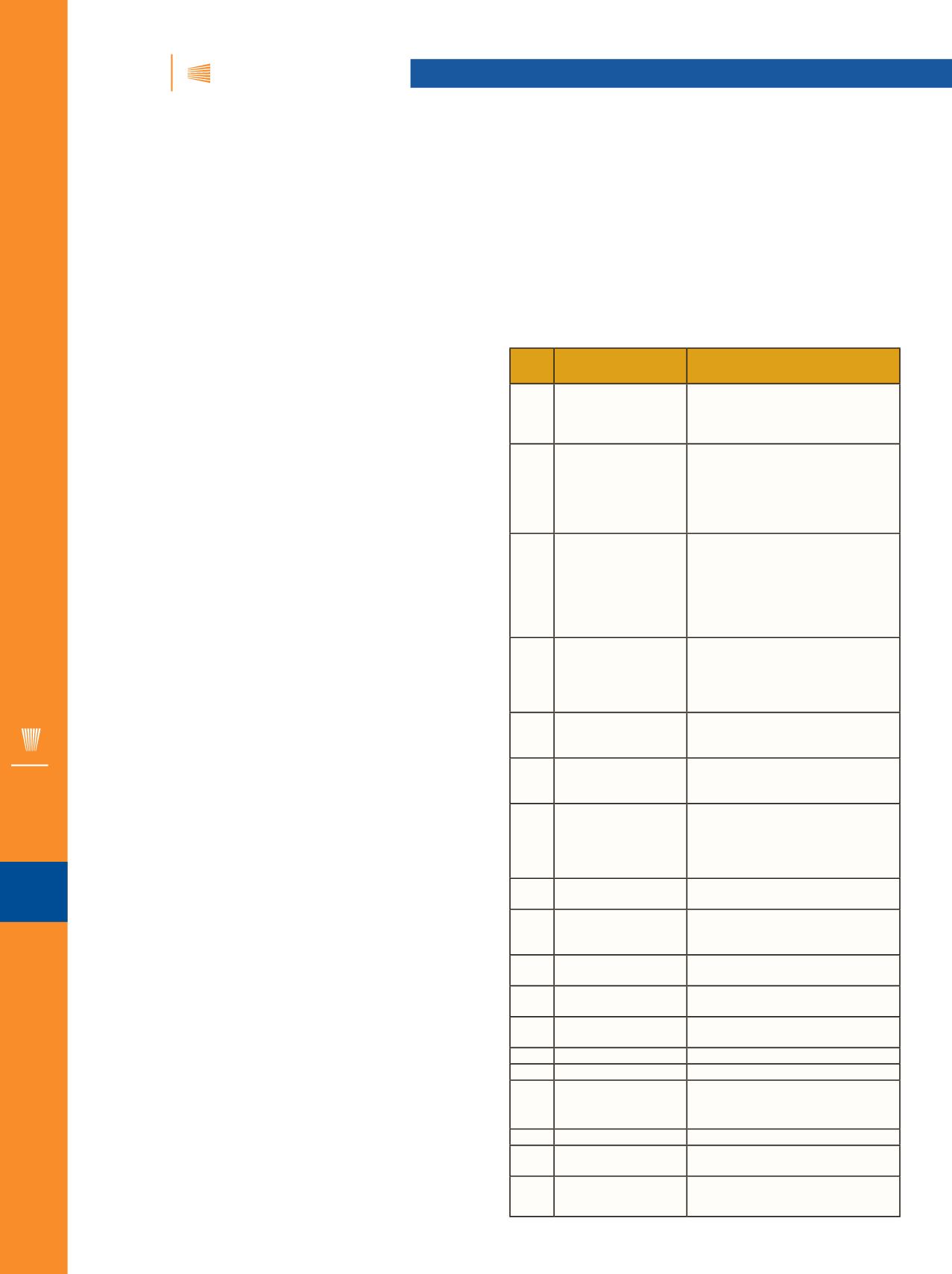
coatings development. As an overview, Table 1 provides an
exhaustive list of all the characterization techniques that can
be used for cold spray coating characterization. The table also
lists the key aspect of each technique and its relevance to
cold spray coating characterization. Not all of the techniques
listed have been used to their optimum level in developing a
complete understanding of the complex nature of a cold spray
coating.
This new series will emphasize the advanced micro-
structural characterization techniques that are used in high-
pressure cold spray coating characterization, including residu-
al stress characterization. Future article installments will also
discuss the preliminary screening tool of hardness and bond
adhesion strength, as well as a distinction between surface
and bulk characterization techniques and their importance
for cold spray coatings. Further, each article will explore a dif-
ferent characterization method, including a note on sample
preparation for characterization, which is critical and must be
followed for accurate results without any artifacts.
iTSSe
For more information:
Dheepa Srinivasan is a principal en-
gineer at GE Power, GE India Technology Center, Bangalore,
dheepa.srinivasan@ge.com,
www.ge.com. This article series is
adapted from
Chapter 5, Cold Spray—Advanced Characteriza-
tion
, inHigh Pressure Cold Spray—Principles and Applications,
edited by Charles M. Kay and J. Karthikeyan (ASM, 2016).
No. Characterization
technique
Key aspect for cold-sprayed
coating
1
Optical microscopy
Coating thickness, coating porosity,
substrate-coating interface
integrity, coating porosity after heat
treatment
2
X-ray diffraction
Feedstock powder phase evolution,
as-sprayed and heat treated coating
phase formation, coating macro-
and microstrain, coating relaxation
behavior, presence of any coating
texture
3
Scanning electron
microscopy
lntersplat interactions in the
sprayed coating before and after
heat treatment, microcracks
and micropores, coating fracture
surface, inclusions and other
phases in the coating or substrate-
coating interface
4
Focused ion beam
Preparation-specific sections for
examination in the scanning and
transmission electron microscopes,
coating splat interface or coating-
substrate interface
5
Electron probe
microanalysis
Precise chemistry, diffusion layers
in a cold-sprayed coating, coating-
substrate interface chemistry
6
Transmission
electron microscopy
Phase identification, dislocation
structure, recovery processes and
recrystallization, coating chemistry
7
Electron
backscattered
diffraction
Coating texture, extent of
recrystallization, deformation
map in the substrate, nature of
bonding in the coating and coating
substrate, grain size and orientation
8 Electron channeling
contrast
Dislocation structure, deformation
characteristics
9
Residual stress
Residual stress in the as-sprayed
coating, coating relaxation process
monitoring
10 X-ray photoelectron
spectroscopy
Chemical bonding, presence of
oxides
11
X-ray fluorescence
Presence of oxide and nature of
chemistry on coating surface
12
Auger electron
spectroscopy
Surface chemistry of the coating
13 Raman spectroscopy
Phase transitions in the coating
14
Oxygen analysis
Feedstock powder characterization
15 Surface roughness
As-sprayed coating, distinguishing
between process parameters, gas
type
16
Microhardness
Screening tool for coating
17
Nanoindentation
Coating characterization,
deformation
18 Bond adhesion test
Evaluating the adhesion and
cohesion strength of the coatings
TABLE 1
—
CHARACTERIZATION TECHNIQUES USED FOR
COLD SPRAY COATINGS AND THEIR KEY ATTRIBUTES