iTSSe
TSS
A D V A N C E D
M A T E R I A L S
&
P R O C E S S E S | F E B R U A R Y / M A R C H
2 0 1 7
4 5
iTSSe
TSS
13
The
Journal of Thermal Spray Technol-
ogy (JTST),
the official journal of the
ASM Thermal Spray Society, publishes
contributions on all aspects—funda-
mental and practical—of thermal spray
science, including processes, feedstock
manufacture, testing, and characteri-
zation. As the primary vehicle for ther-
mal spray information transfer, its mission is to synergize
the rapidly advancing thermal spray industry and related
industries by presenting research and development efforts
leading to advancements in implementable engineering
applications of the technology. Articles from the January is-
sue, as selected by
JTST
Editor-in-Chief Armelle Vardelle, are
highlighted here. This issue will feature papers based on pre-
sentations at ITSC 2016. In addition to the print publication,
JTST
is available online through springerlink.com. For more
information, visit asminternational.org/tss.
THERMAL CYCLING BEHAVIOR OF QUASI-
COLUMNAR YSZ COATINGS DEPOSITED BY
PS-PVD
Jiasheng Yang, Huayu Zhao, Xinghua Zhong, Fang Shao,
Chenguang Liu, Yin Zhuang, Jinxing Ni, and Shunyan Tao
Columnar-structured thermal barrier coatings, due
to their high strain tolerance, are expected to substantially
extend turbine lives and improve engine efficiencies. In this
paper, a plasma spray-physical vapor deposition (PS-PVD)
process was used to deposit yttria partially stabilized zirco-
nia (YSZ) coatings with quasi-columnar structures. Thermal
cyclic tests on burner rigs and thermal shock tests using a
coating surface during burner rig tests with the coating sur-
face temperature of ~1250°C. Failure of the coating is mainly
due to the break and pullout of center columnar segments
(Fig. 1).
HOT CORROSION MECHANISM IN MULTILAYER
SUSPENSION PLASMA SPRAYED GD2ZR2O7/
YSZ THERMAL BARRIER COATINGS IN THE
PRESENCE OF V
2
O
5
+ NA
2
SO
4
Krishna Praveen Jonnalagadda, Satyapal Mahade,
Nicholas Curry, Xin-Hai Li, Nicolaie Markocsan, Per Nylén,
Stefan Björklund, and Ru Lin Peng
This study investigates corrosion resistance of two-
layer Gd
2
Zr
2
O
7
/YSZ, three-layer dense Gd
2
Zr
2
O
7
/ Gd
2
Z
r2
O
7
/
YSZ, and a reference single-layer YSZ coating with a similar
overall top coat thickness of 300-320 µm. All coatings were
manufactured by suspension plasma spraying resulting in
a columnar structure except for the dense layer. Corrosion
tests were conducted at 900°C for 8 h using V
2
O
5
and Na
2
SO
4
as corrosive salts at a concentration of approximately 4 mg/
cm
2
. SEM investigations after the corrosion tests show that
Gd
2
Zr
2
O
7
-based coatings exhibited lower reactivity with the
corrosive salts and the formation of gadolinium vanadate
(GdVO
4
) accompanied by the phase transformation of zir-
conia was observed. It is believed that the GdVO
4
formation
between the columns reduced the strain tolerance of the
coating. Further, due to the fact that Gd
2
Zr
2
O
7
has a lower
fracture toughness value, this made it more susceptible to
corrosion-induced damage. In addition, presence of a rela-
tively dense layer of Gd
2
Zr
2
O
7
on the top did not help reduce
corrosion-induced damage. For the reference YSZ coating,
the observed corrosion-induced damage was lower, proba-
bly due to a combination of more limited salt penetration,
the SPS microstructure, and superior fracture toughness of
YSZ (Fig. 2).
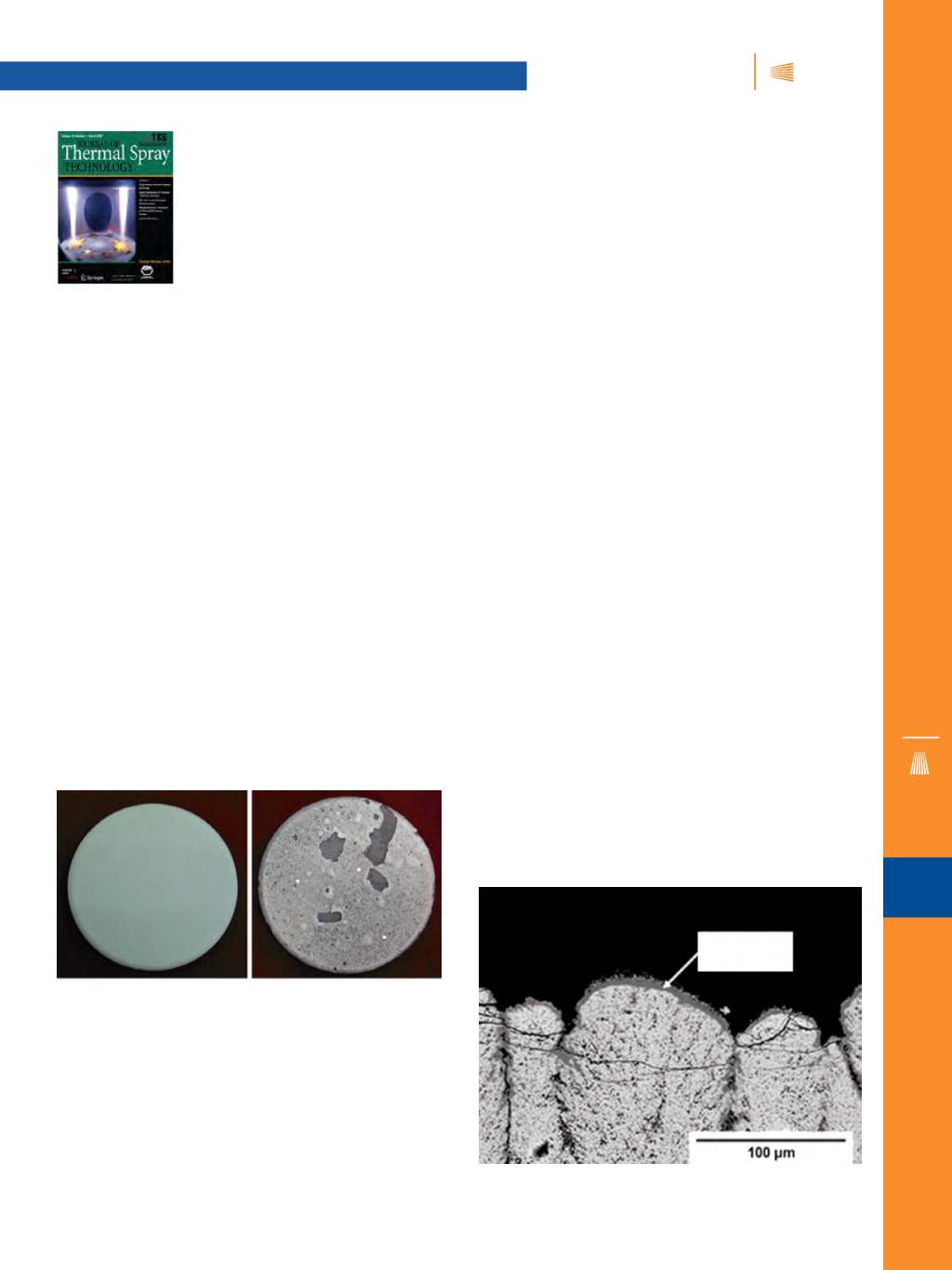
Fig. 1 —
Photographs of YSZ TBCs (a) before and (b) after thermal
cycling for 623 cycles.
Fig. 2 —
Cross-section of two-layer gadolinium zirconate coatings
showing GdVO
4
on the top surface.
JTST
HIGHLIGHTS
GdVO
4
(a)
(b)
B
heating and water-quenching method were applied to eval-
uate the thermal cycling and thermal shock behaviors of
structured thermal barrier coatings (TBCs). Evolution of the
microstructures, phase composition, residual stresses, and
failure behaviors of quasi-columnar YSZ coatings before and
after thermal tests was investigated. The quasi-columnar
coating obtained had an average life of around 623 cycles
when the spallation area reached about 10% of the total
C
A