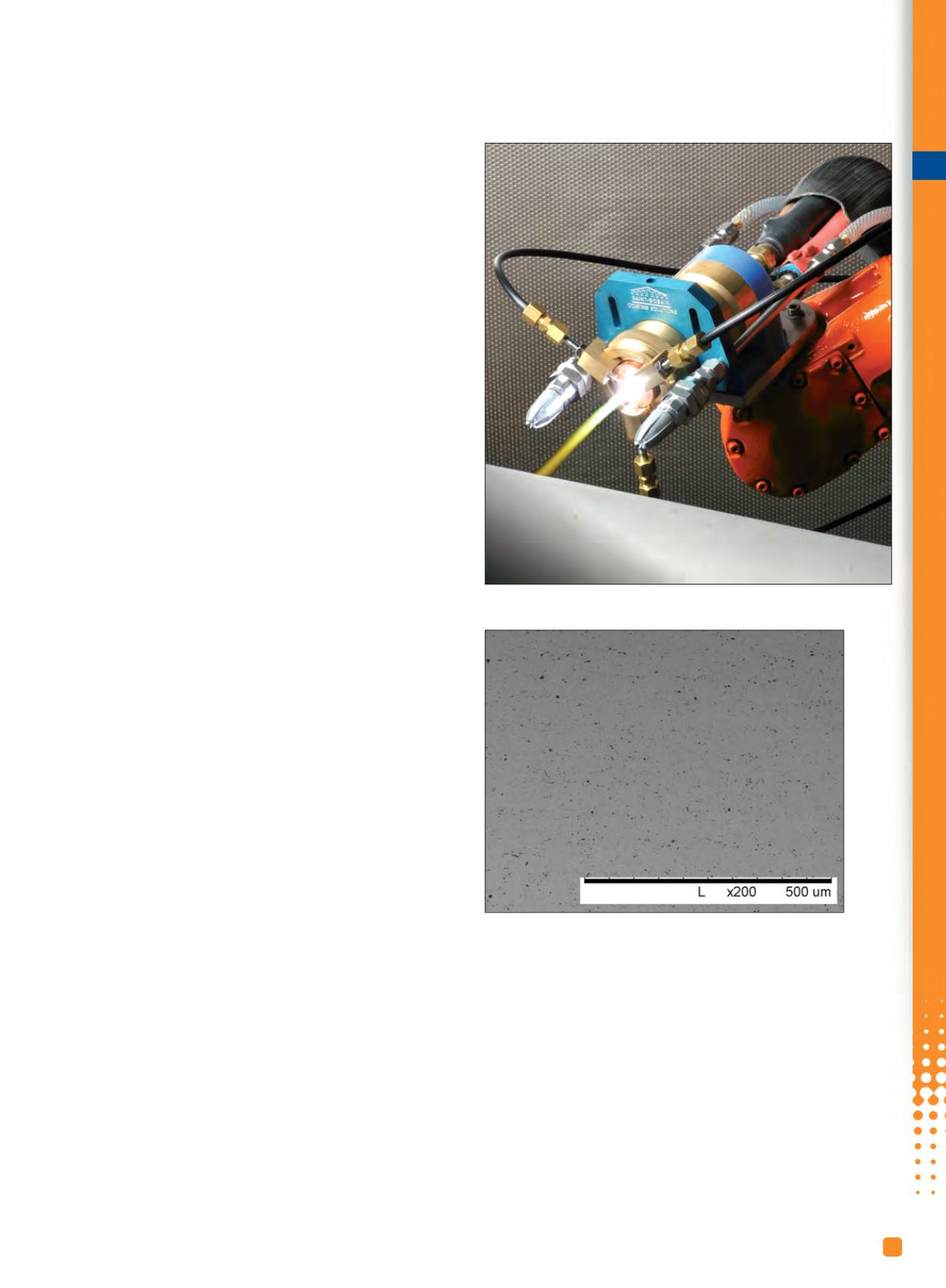
T
hermal spray applications in the gas turbine-power
generation industry are among the most established
uses for this technology, in addition to widespread appli-
cations in the petroleum industry. However, several chal-
lenges exist with regard to conventional gas turbines.
These include the need for higher temperature thermal
barrier coatings (TBCs), CMAS-resistant overlays, and
cost reduction.
The first two challenges are related to new material
and coating development, which increases per component
cost. The competitive nature of the thermal spray indus-
try does not offer much variation in feedstock prices.
Therefore, thermal spray applicators must concentrate on
efficiency improvements to reduce costs. One strategy—
increasing deposition efficiency—lowers both powder
and labor costs. However, although this approach offers
some savings, higher spray rates at higher efficiencies are
most beneficial.
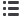
Recognizing the need for a cost-efficient plasma gun
capable of high deposition rates, Saint-Gobain, France,
worked to develop a commercially available solution
called the ProPlasma gun. Engineers analyzed both gun
components and gas flow dynamics to design a gun that
improves plasma stability. The gun was developed based
on a pre-existing design, so that the new torch can be im-
plemented on available controllers and power supplies.
ProPlasma also increases electrode life per kilogram of
deposited material.
Considerable effort was spent on characterization of Pro-
Plasma sprayed, yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) for thermal
barrier applications. The coating was sprayed at 150 g/min
at 57% efficiency versus 40-60 g/min for the F4 system. This
translates to roughly 25% savings in powder and 40% sav-
ings in combined labor, energy, and powder costs. The in-
creased efficiency and cost savings is critical due to a
gradual change to TBCs based on zirconia and doped with
more expensive rare earth elements such as gadolinium.
Similar trends regarding improved deposition efficien-
cies are noted for materials in non-power related industries
as well. Of particular interest is plasma sprayed yttria. This
material is widely used to protect chamber components
from erosion in the reactive ion etching process in semi-
conductor fabrication. For this application, critical factors
include coating quality (very high density, lower probabil-
ity of particle release) and related costs. Yttria is an expen-
sive material, and therefore deposition efficiency is critical.
Combining the ProPlasma gun with a specially devel-
oped yttria powder is highly efficient. Traditional yttria
powders available for this application are made using ag-
glomeration and sintering. As another option, Saint-Gob-
ain’s newly patented DEnsitY yttria powder is narrow
sized, plasma densified, and exhibits very high purity
(>99.98%). This powder melts more easily in the plasma,
enabling higher coating densities. Deposition efficiency
improvements between 10-15% were achieved using the
new powder in conjunction with an F4 torch, and up to
30% when combined with the ProPlasma gun, which al-
lows even higher spray rates. For example, a 100% in-
crease can be achieved for optimized coatings: 25 g/min
for the F4 versus 50 g/min for the ProPlasma. A mi-
crostructure of the optimized coating is shown in Fig. 2.
As the thermal spray industry grows, particularly in the
power generation field, solutions that deposit coatings with
torches capable of high deposition efficiencies and spe-
cially engineered powder morphologies enhancing depo-
sition rates will have a competitive advantage.
iTSSe
For more information:
Shari Fowler-Hutchinson is product
sales development manager, Saint Gobain, 1 New Bond St.,
M/S 525-203, Worcester, MA 01615, 508/795-5908,
shari. fowler-hutchinson@saint-gobain.com,
www.saint-gobain.com.
i
T
S
S
e
5
ADVANCED MATERIALS & PROCESSES •
MAY 2014
49
CASE STUDY
Improving Deposition Rate Efficiency
Fig. 1 —
The ProPlasma gun is capable of high deposition rates and
is designed to improve plasma stability.
Fig. 2 —
Microstructure of the optimized coating.