Improving superalloy performance
Work from Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Ma-
terialien and Energie (HZB), and University of Mün-
ster, both in Germany, shows how new phases in a
nickel-base alloy form and evolve, offering clues to
how high-performance alloys could be improved.
Researchers combined transmission electron mi-
croscopy (TEM) and atom probe tomography (APT)
to accomplish this. The microstructure of nickel-
base alloys changes under controlled aging or heat
treatment and in the classical two-phase microstruc-
ture new phases are initially formed. Researchers
precisely observed the phase separation process on
the atomic scale for the first time.
To do so, they simulated the aging process of the
alloy by heat treating it for different periods. They
documented how the microstructure changed dur-
ing aging by using micrographs from the TEM.
Whereas the classical two-phase microstructure
consists of cuboid γ’ precipitates embedded in a so
called γ-matrix, during heat treatment, spherical γ particles initially form in the γ’ precip-
itates of the alloy, and then further coalesce into plates that finally split the γ’ precipitates.
The thermo-mechanical properties of these types of alloys depend largely on the stability
of this γ/γ’ microstructure.
www.helmholtz-berlin.de/index_en.html.FDA approval for guidewire
MediValve Ltd., Israel, received 510(k) pre-marketing clearance from the U.S. Food
and Drug Administration for its acWire guidewire, intended for use in peripheral vascu-
lar and heart catheterization procedures, to introduce
and assist in positioning diagnostic and interventional
devices. The guidewire may also function as an align-
ment tool by providing a reference plane of the
anatomical structure of interest. It is a single-use, fully
disposable medical device that uses shape-memory
alloy technology to enable identification of cardiovas-
cular structures using existing imaging methods. The
device is intended for implantation plane acquisition,
during trans-catheter aortic-valve implantation
(TAVI) procedures using fluoroscopic imaging.
www.medivalve.com.
Plastics machinery safety standards update
The Plastics Industry Trade Association, Washington, and the American National
Standards Institute (ANSI) announce the publication of two recently revised and ap-
proved American National Standards on plastics machinery safety: ANSI/SPI B151.20 -
2013 Safety Requirements for Plastics Sheet Production Machinery, and ANSI/SPI
B151.27 - 2013 Safety Requirements for the Integration of Robots with Injection Mold-
ing Machines, both of which address detailed safety requirements for the specific ma-
chine or group of machines.
B151.20 specifies requirements for the manufacture, care, and use of plastics sheet pro-
duction machinery to minimize hazards to personnel associated with machine activity.
B151.27 addresses the integration, care, and use of robots used with injection molding ma-
chines to minimize hazards to personnel associated with robot and machine activity.
www.plasticsindustry.org,
www.ansi.org.
news
industry
briefs
Duke University’s Pratt School of
Engineering,
Durham, N.C.,
researchers used computational
methods to identify dozens of
platinum-group alloys with
databases and algorithms that took
years to develop. Using theories
about how atoms interact to model
chemical structures from the
ground up, thousands of potential
materials were screened for high
probabilities of stability. After
nearly 40,000 calculations, results
identified 37 new binary alloys in
the platinum-group metals, which
include osmium, iridium,
ruthenium, rhodium, platinum, and
palladium. These metals are prized
for their catalytic properties,
resistance to chemical corrosion,
and performance in high-
temperature environments.
www.pratt.duke.edu.
Porous Power Technologies LLC
(PPT),
Boulder, launched
Symmetrix NC2020, a ceramic
battery separator designed to
improve thermal stability and
safety of large-format lithium-ion
batteries. The separator is
nonflammable and more resistant
to shrinkage than conventional
separators, making cells more
stable when damaged or abused.
The ceramic particles are blended
with PVDF polymer to form a
flexible, ceramic-rich microporous
membrane. Ions flow freely
through the open pore structure,
enabling cells with good power
over broad temperature ranges.
The sponge-like membrane
conforms to the electrode surface
to prevent dead spots and ensure
reliable performance, even as
electrodes expand and contract
over many cycles.
M
ETALS
P
OLYMERS
C
ERAMICS
ADVANCED MATERIALS & PROCESSES •
MARCH 2014
6
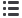
3D reconstruction of an atom probe
measurement. The
g
matrix (purple)
is surrounding the cuboidal
g
’
precipitates (green). Only a few
nanometer-sized
g
platelets are seen
in the
g
’
precipitates. APT allows
site-specific analysis of the structure
at the atomic scale and reveals the
chemical composition in
measurements of individual areas.
Courtesy of HZB.
MediValve receives FDA 510(k)
approval for acWire guidewire.
Courtesy of MediValve Ltd.